Introduction
There have been many discussions on Stack Overflow and GitHub around implementing infinite scroll using React Native, on top of FlatList or SectionList. I've found that there aren't any easy solution out there for bidirectional infinite scroll for React Native. Recently, while working on v3.0.0 of React Native Chat SDK at Stream, we had to add bidirectional infinite scroll to our chat components. We had to jump through plenty of hurdles to make it happen while maintaining a good user experience around scrolling. Thus we decided to publish an excellent and small open-source package, to make this task easier for other React Native developers.
- GitHub github.com/GetStream/react-native-bidirectional-infinite-scroll/
- NPM npmjs.com/package/react-native-bidirectional-infinite-scroll
The FlatList can be used like this:
import { FlatList } from "react-native-bidirectional-infinite-scroll";
<FlatList
data={numbers}
renderItem={ListItem}
keyExtractor={(item) => item.toString()}
onStartReached={onStartReached} // required, should return a promise
onEndReached={onEndReached} // required, should return a promise
showDefaultLoadingIndicators={true} // optional
onStartReachedThreshold={10} // optional
onEndReachedThreshold={10} // optional
activityIndicatorColor={'black'} // optional
HeaderLoadingIndicator={() => { /** Your loading indicator */ }} // optional
FooterLoadingIndicator={() => { /** Your loading indicator */ }} // optional
// You can use any other prop on react-native's FlatList
/>
Jump Ahead
What and How
This section will walk you through the hurdles of implementing bidirectional infinite scroll and how we solved them.
Support for onStartReached
FlatList from React Native has built-in support for infinite scroll in a single direction (from the end of the list). You can add a prop onEndReachedon FlatList. This function gets called when your scroll is near the end of the list, and thus you can append more items to the list from this function. You can Google for React Native infinite scrolling, and you will find plenty of examples for this. Unfortunately, the FlatList doesn't provide any similar prop for onStartReached for infinite scrolling in other directions.
We have added support for this prop as part of this package by simply adding the onScroll handler on FlatList, and executing the callback function (onStartReached) when the scroll is near the start of the list. If you take a look at the implementation of VirtualizedList, you will notice that onEndReachedfunction gets called only once per content length. That's there for a good purpose - to avoid redundant function calls on every scroll position change. Similar optimizations have been done for onStartReached within this package.
Race condition between onStartReached and onEndReached
To maintain a smooth scrolling experience, we need to manage the execution order of onStartReached and onEndReached. Because if both the callbacks happen at (almost) the same time, which means items will be added to the list from both directions, which may result in scroll jump - which is not a good UX. Thus it's essential to make sure one callback waits for the other callback to finish.
onStartReachedThreshold and onEndReachedThreshold
FlatList from React Native has a support for the prop onEndReachedThreshold, which is documented here.
How far from the end (in units of visible length of the list) the bottom edge of the list must be from the end of the content to trigger the
onEndReachedcallback.
Instead, it's easier to have a fixed value offset (distance from the end of the list) to trigger one of these callbacks. Thus we can maintain these two values within our implementation. So onStartReachedThreshold and onEndReachedThreshold props accept the number - distance from the end of the list to trigger one of these callbacks.
Smooth scrolling experience
FlatList from React Native accepts a prop - maintainVisibleContentPosition, which makes sure your scroll doesn't jump to the end of the list when more items are added to the list. But this prop is only supported on iOS for now. So taking some inspiration from this PR, we published our separate package to add support for this prop on Android - flat-list-mvcp. And thus @stream-io/flat-list-mvcp is a dependency of the react-native-bidirectional-scroll package.
Tutorial: Chat UI With Bidirectional Infinite Scroll
Now let's see how we can implement a chat message list, scrolling infinitely in both directions.
Setup
Lets start by creating a React Native app:
$ npx react-native init AwesomeChatList
$ cd AwesomeChatListAdd the required dependencies:
$ yarn add react-native-bidirectional-infinite-scroll @stream-io/flat-list-mvcpNext, run the app:
$ npx react-native run-iosNote: The server will auto-refresh as you make changes to the code.
Create message list
Open this project in some editor (I love VS Code) and open App.js in the project's root directory.
We are going to populate the list with dummy messages. In a real application, these messages are queried against a server. For example, we can write a simple utility function to mock this API call for querying n number of messages.
Create a file - utils.js
// Generate random integer, we will use this to use random message from list of dummy messages.
export const getRandomInt = (min: number, max: number) => {
return Math.floor(Math.random() * (max - min)) + min;
};
// Generate unique key for message component of FlatList.
export const generateUniqueKey = () =>
`_${Math.random().toString(36).substr(2, 9)}`;
// List of test messages to generate chat data.
export const testMessages = [
'Hey, where were you yesterday? I was trying to call you',
'Yeah dude!! Had a really bad night. I was really hungover',
'lol, thats so typical you. Who did you go out with?',
'Dont even ask me about it, I am never going drink with Uthred again. That dude is a beast',
'hahahaha, I can totally imagine!!',
'Ciao :)',
];
export type Message = {
id: string;
text: string;
isMyMessage: boolean;
};
/**
* Mocks the api call to query `n` number of messages.
* We are going to add some timeout before returning the result to simulate an api call over network.
*
* We are going to generate two types of message:
* - sent message
* - received message
*
* This will be controlled by a boolean property on message object - `isMyMessage`.
* This will be randomly assigned to message, based on result of getRandomInt.
* These two messages will be styled differently, which is the case for most of the
* popular messaging applications e.g., whatsapp, messenger
*
* @param n {number} Number of new messages to query
* @param networkLatency {number} Number of milliseconds, to simulate api call.
*/
export const queryMoreMessages: (
n: number,
networkLatency?: number
) => Promise<Array<Message>> = (n, networkLatency = 100) => {
return new Promise((resolve) => {
const newMessages: Array<Message> = [];
for (let i = 0; i < n; i++) {
const messageText = testMessages[getRandomInt(0, testMessages.length)];
newMessages.push({
id: generateUniqueKey(),
text: messageText,
isMyMessage: Boolean(getRandomInt(0, 2)), // Randomly assign true or false.
});
}
// Lets resolve after 500 ms, to simulate network latency.
setTimeout(() => {
resolve(newMessages);
}, networkLatency);
});
};
Next, let's write a small UI component for the message bubble. Create a file named MessageBubble.js.
https://gist.github.com/vishalnarkhede/22394f80d629daea1f438ddf42a10ba0
Now let's first implement a simple list, which renders these messages on the first load. Copy the following content to App.js and hit save.
import React, {useEffect, useState} from 'react';
import {SafeAreaView, StyleSheet, Text, View} from 'react-native';
import {FlatList} from 'react-native-bidirectional-infinite-scroll';
import {MessageBubble} from './MessageBubble';
import {queryMoreMessages} from './utils';
const App = () => {
const [messages, setMessages] = useState();
useEffect(() => {
// When app is opened, we are going to render 50 messages on screen.
// Generally this is where you connect to chat server and query first batch of messages.
const initChat = async () => {
const initialMessages = await queryMoreMessages(50, 0);
setMessages(initialMessages);
};
initChat();
}, []);
if (!messages) {
// If the messages are not ready, lets not show anything.
// Generally you can render some kind of loading indicator in this case.
return null;
}
return (
<SafeAreaView style={styles.safeArea}>
<View style={styles.header}>
<Text style={styles.headerTitle}>Chat between two users</Text>
</View>
<FlatList data={messages} inverted renderItem={MessageBubble} />
</SafeAreaView>
);
};
const styles = StyleSheet.create({
header: {
alignItems: 'center',
paddingVertical: 10,
borderBottomColor: '#BEBEBE',
borderBottomWidth: 1,
},
headerTitle: {fontSize: 20, fontWeight: 'bold'},
safeArea: {
flex: 1,
},
});
export default App;
You should be able to see the list of messages as shown in the screenshot on the right.
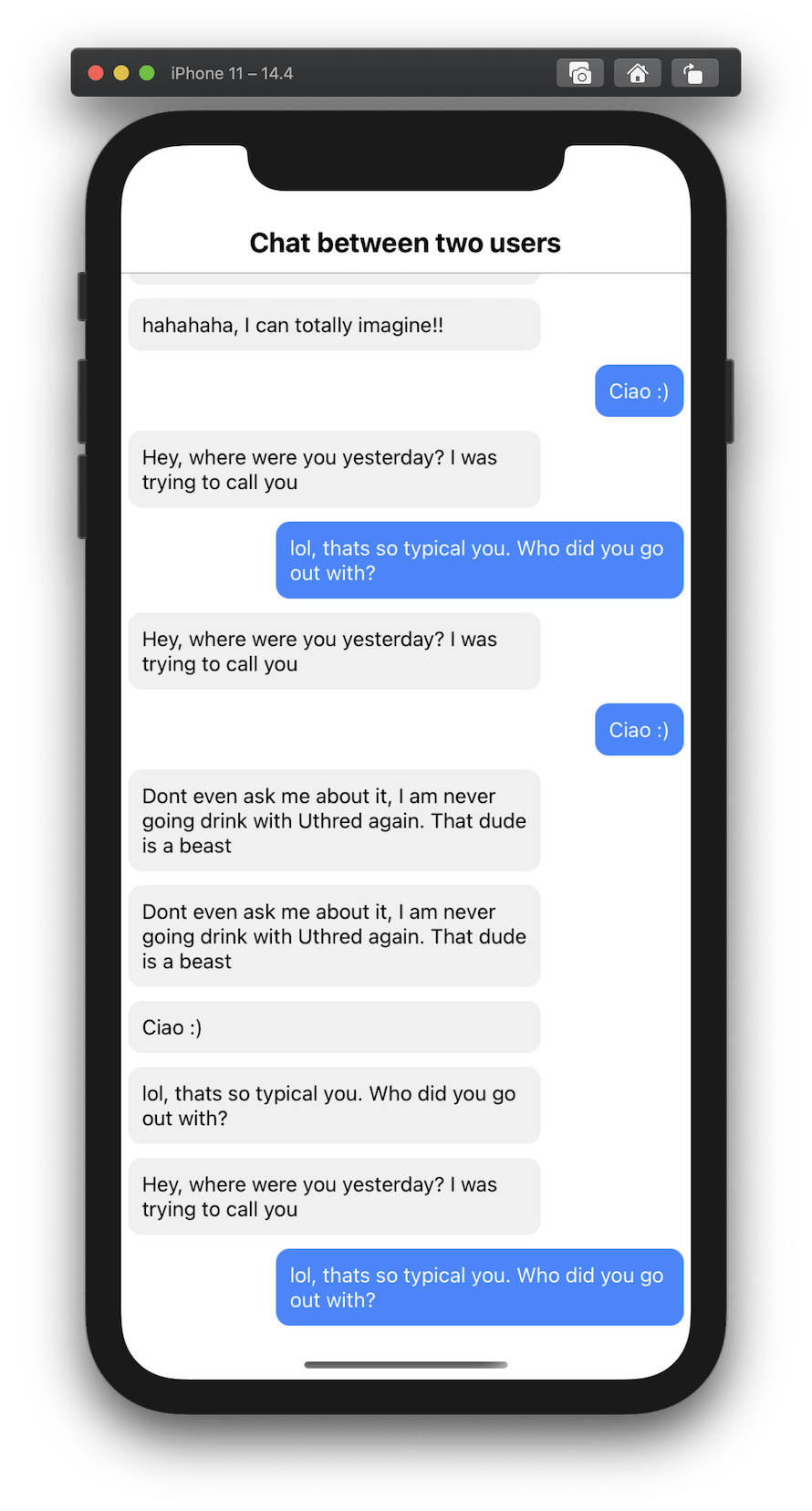
Add Infinite Scroll
Next, let's implement infinite scroll to the list by adding onStartReached and onEndReached prop functions.
onStartReached- add 10 messages at the beginning of the listonEndReached- add 10 messages at the end of the list
Replace the contents of App.js with the following:
import React, {useEffect, useState} from 'react';
import {SafeAreaView, StyleSheet, Text, View} from 'react-native';
import {FlatList} from 'react-native-bidirectional-infinite-scroll';
import {MessageBubble} from './MessageBubble';
import {queryMoreMessages} from './utils';
const App = () => {
const [messages, setMessages] = useState();
useEffect(() => {
// When app is opened, we are going to render 50 messages on screen.
// Generally this is where you connect to chat server and query first batch of messages.
const initChat = async () => {
const initialMessages = await queryMoreMessages(50, 0);
setMessages(initialMessages);
};
initChat();
}, []);
// Add 10 more messages to end of the list.
// In real chat application, this is where you have your pagination logic.
const loadMoreOlderMessages = async () => {
const newMessages = await queryMoreMessages(10);
setMessages((m) => {
return m.concat(newMessages);
});
};
// Add 10 more messages to beginning of the list.
// In real chat application, this is where you have your pagination logic.
const loadMoreRecentMessages = async () => {
const newMessages = await queryMoreMessages(10);
setMessages((m) => {
return newMessages.concat(m);
});
};
if (!messages) {
// If the messages are not ready, lets not show anything.
// Generally you can render some kind of loading indicator in this case.
return null;
}
/**
* NOTE:
*
* - You can also control the scroll offset, at which `onEndReached` and `onStartReached`
* should be called, using props - onEndReachedThreshold and onStartReachedThrehols
* - We are using `inverted` FlatList, since thats a common UX for Chat applications.
*/
return (
<SafeAreaView style={styles.safeArea}>
<View style={styles.header}>
<Text style={styles.headerTitle}>Chat between two users</Text>
</View>
<FlatList
data={messages}
inverted
onEndReached={loadMoreOlderMessages}
onStartReached={loadMoreRecentMessages}
renderItem={MessageBubble}
/>
</SafeAreaView>
);
};
const styles = StyleSheet.create({
header: {
alignItems: 'center',
paddingVertical: 10,
borderBottomColor: '#BEBEBE',
borderBottomWidth: 1,
},
headerTitle: {fontSize: 20, fontWeight: 'bold'},
safeArea: {
flex: 1,
},
});
export default App;
And that's it. If you scroll up or down, you will see new messages being loaded in the list and scroll position being maintained as well (both for Android and iOS)
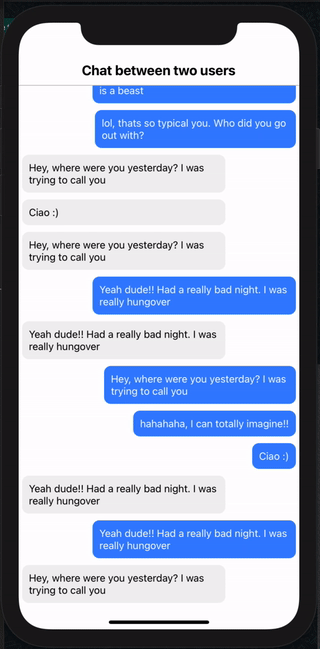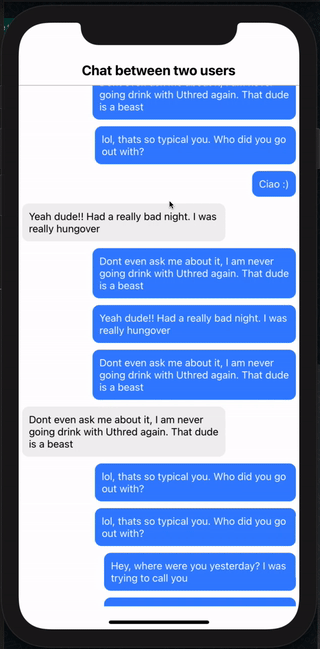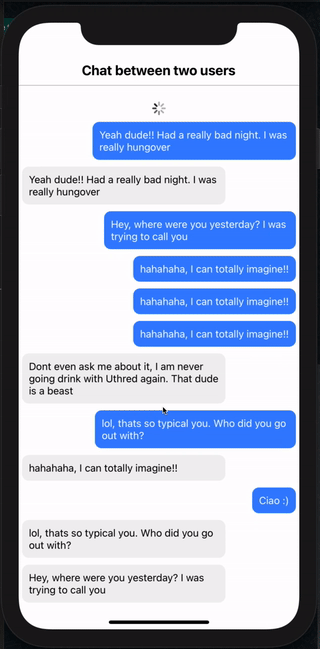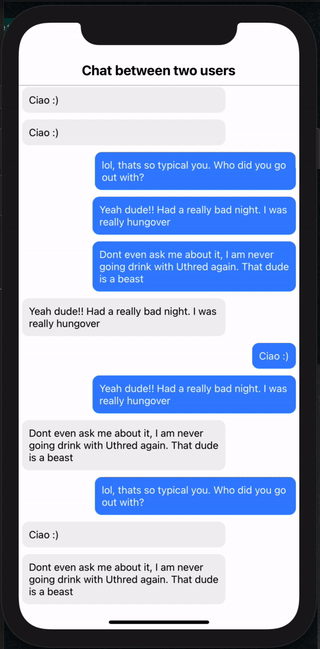
Send Message
In real chat applications, you don't actually "infinitely" scroll. There is always an end to the loadMoreRecentMessages function. And after this point, you will want the scroll to automatically move to the bottom of the list, as other users send a new message or if you send a new message.
Basically, after this point, we want to enable the "autoscroll to top" (bottom in our case, since the list is inverted) functionality of FlatList. You can do this by setting a prop enableAutoscrollToTop as true. Additionally, you can also set autoscrollToTopThreshold to true.
-
Let's try to simulate this scenario by keeping a counter on the number of times recent messages were queried. Once the counter crosses 2, let's stop querying the message.
-
Let's add a "Send Message" button at the bottom to send a single message.
Replace the contents of App.js with following
import React, {useEffect, useState} from 'react';
import {
SafeAreaView,
StyleSheet,
Text,
Touchable,
TouchableOpacity,
View,
} from 'react-native';
import {FlatList} from 'react-native-bidirectional-infinite-scroll';
import {MessageBubble} from './MessageBubble';
import {queryMoreMessages} from './utils';
// Counter to keep track of how many times `loadMoreRecentMessages` function has been called.
// We want to simulate a UX where user has scrolled till the most recent message available in
// chat. So for our example, we are going stop querying (and appending) new messages to the screen,
// once loadMoreRecentCounter is greater than 2.
// In real chat applications, you generally receive a flag from pagination api, which tells the app
// if user is at the most recent message in chat or not.
let loadMoreRecentCounter = 0;
const App = () => {
const [messages, setMessages] = useState();
const [enableAutoscrollToTop, setEnableAutoscrollToTop] = useState(false);
useEffect(() => {
// When app is opened, we are going to render 50 messages on screen.
// Generally this is where you connect to chat server and query first batch of messages.
const initChat = async () => {
const initialMessages = await queryMoreMessages(50, 0);
setMessages(initialMessages);
};
initChat();
}, []);
// Add 10 more messages to end of the list.
// In real chat application, this is where you have your pagination logic.
const loadMoreOlderMessages = async () => {
const newMessages = await queryMoreMessages(10);
setMessages((m) => {
return m.concat(newMessages);
});
};
// Add 10 more messages to beginning of the list.
// In real chat application, this is where you have your pagination logic.
const loadMoreRecentMessages = async () => {
if (loadMoreRecentCounter > 2) {
// User is at the most recent message in chat.
!enableAutoscrollToTop && setEnableAutoscrollToTop(true);
return;
}
const newMessages = await queryMoreMessages(10);
setMessages((m) => {
return newMessages.concat(m);
});
loadMoreRecentCounter += 1;
};
/**
* Simulates a send message feature of Chat applications. It simply adds a randomly
* generated message at beginning of the list - it can either be a sent or received message.
*/
const sendMessage = async () => {
const newMessages = await queryMoreMessages(1, 0);
setMessages((m) => {
return newMessages.concat(m);
});
};
if (!messages) {
// If the messages are not ready, lets not show anything.
// Generally you can render some kind of loading indicator in this case.
return null;
}
/**
* NOTE:
*
* - You can also control the scroll offset, at which `onEndReached` and `onStartReached`
* should be called, using props - onEndReachedThreshold and onStartReachedThrehols
* - We are using `inverted` FlatList, since thats a common UX for Chat applications.
*/
return (
<SafeAreaView style={styles.safeArea}>
<View style={styles.header}>
<Text style={styles.headerTitle}>Chat between two users</Text>
</View>
<FlatList
data={messages}
inverted
enableAutoscrollToTop={enableAutoscrollToTop}
onEndReached={loadMoreOlderMessages}
onStartReached={loadMoreRecentMessages}
renderItem={MessageBubble}
/>
<TouchableOpacity onPress={sendMessage} style={styles.sendMessageButton}>
<Text style={styles.sendButtonTitle}>Send message</Text>
</TouchableOpacity>
</SafeAreaView>
);
};
const styles = StyleSheet.create({
header: {
alignItems: 'center',
paddingVertical: 10,
borderBottomColor: '#BEBEBE',
borderBottomWidth: 1,
},
headerTitle: {fontSize: 20, fontWeight: 'bold'},
safeArea: {
flex: 1,
},
sendMessageButton: {
width: '100%',
padding: 20,
backgroundColor: '#FF4500',
alignItems: 'center',
},
sendButtonTitle: {
color: 'white',
fontSize: 15,
fontWeight: 'bold',
},
});
export default App;
Now scroll to the bottom couple of times, until you can't load any more recent messages. Now try to send a single message by pressing the "Send Message" button. You will see scroll automatically scrolling to the bottom of the list. But if you scroll up a bit and then send a message - then the scroll position will be maintained. The autoscrollToTopThreshold prop controls this threshold.

Congratulations 🎉
You've implemented a bidirectional infinite scroll with React Native! Additionally following props are available to add more customisations:
- activityIndicatorColor
- enableAutoscrollToTop
- autoscrollToTopThreshold
- onStartReachedThreshold
- onEndReachedThreshold
- showDefaultLoadingIndicators
- HeaderLoadingIndicator
- FooterLoadingIndicator
I hope you found it useful. Feel free to add some questions, comments, and feedback here.

